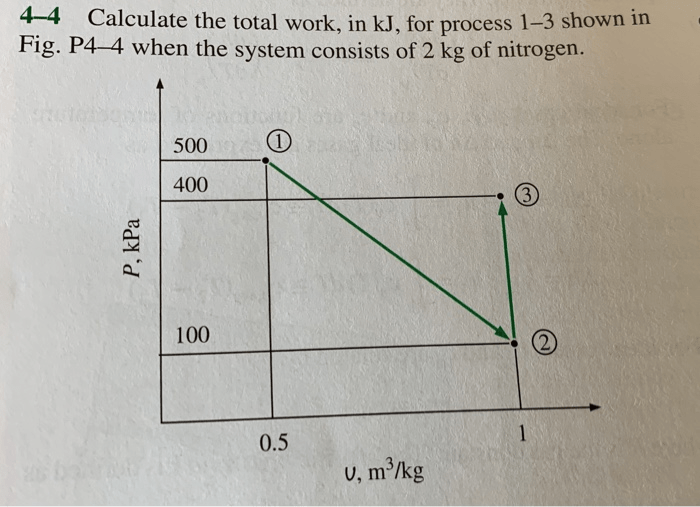
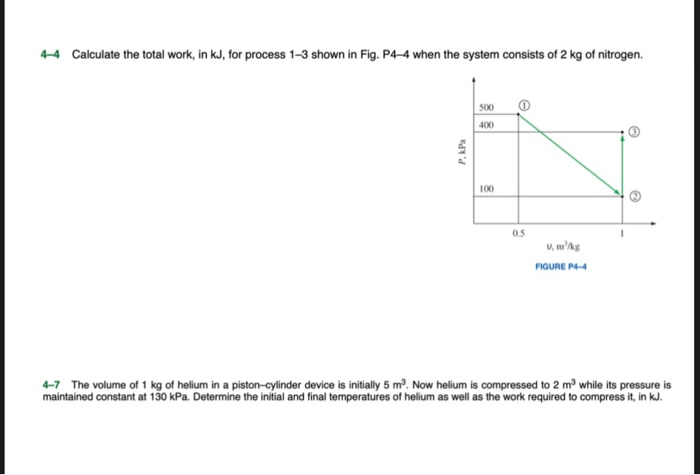
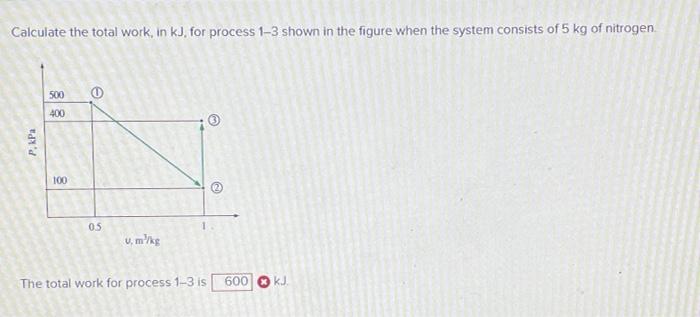
Calculate the total work in kJ for process 1-3, a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, is essential for process analysis and optimization. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of calculating total work, exploring methods, applications, and advanced concepts, empowering readers to delve into the intricacies of work analysis.
Understanding the units of measurement, kilojoules, and the significance of total work calculations sets the stage for exploring various methods to determine work, including the work integral and graphical methods. By comparing and contrasting these approaches, readers gain a deeper understanding of work calculations.
Overview of Calculating Total Work: Calculate The Total Work In Kj For Process 1-3
In thermodynamics, work refers to the energy transfer that occurs when a force acts through a distance. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude and no direction. The SI unit of work is the joule (J), which is defined as the work done when a force of one newton is applied through a distance of one meter.
Calculating total work is essential in process analysis, as it provides insights into the energy requirements and efficiency of a system. Total work can be positive or negative, depending on whether the force is applied in the direction of motion or against it.
Methods for Calculating Total Work, Calculate the total work in kj for process 1-3
There are several methods for calculating total work, including:
- Work integral:This method involves integrating the force with respect to distance. It is the most general method and can be used to calculate work for any type of force.
- Graphical methods:These methods involve using graphs to determine the work done. The most common graphical method is to plot the force-distance curve and calculate the area under the curve. This area represents the total work done.
Applications of Total Work Calculation
Total work calculations have numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Process optimization:By calculating the total work required for a process, engineers can identify areas where efficiency can be improved.
- Evaluating process efficiency:Total work can be used to determine the efficiency of a process by comparing it to the theoretical minimum work required.
- Engineering design:Total work calculations are used in the design of machines and systems to ensure that they are efficient and meet performance requirements.
Advanced Concepts in Total Work Analysis
In addition to the basic concepts of total work, there are several advanced concepts that are important for a deeper understanding of work calculations.
- Reversible and irreversible work:Reversible work is work that can be completely undone without any loss of energy. Irreversible work, on the other hand, is work that cannot be undone without some loss of energy.
- Role of entropy in work calculations:Entropy is a measure of disorder in a system. In thermodynamics, work calculations are often associated with changes in entropy.
- Limitations and assumptions:Total work calculations are based on certain assumptions and limitations. It is important to be aware of these limitations when interpreting the results of work calculations.
FAQ Compilation
What is the significance of calculating total work in process analysis?
Calculating total work provides insights into the energy transfer and conversion within a process, enabling engineers and scientists to optimize processes for efficiency and performance.
How can total work be used to evaluate the efficiency of a process?
Total work calculations serve as a metric to assess the efficiency of a process by comparing the actual work done to the theoretical maximum work, highlighting areas for improvement and optimization.