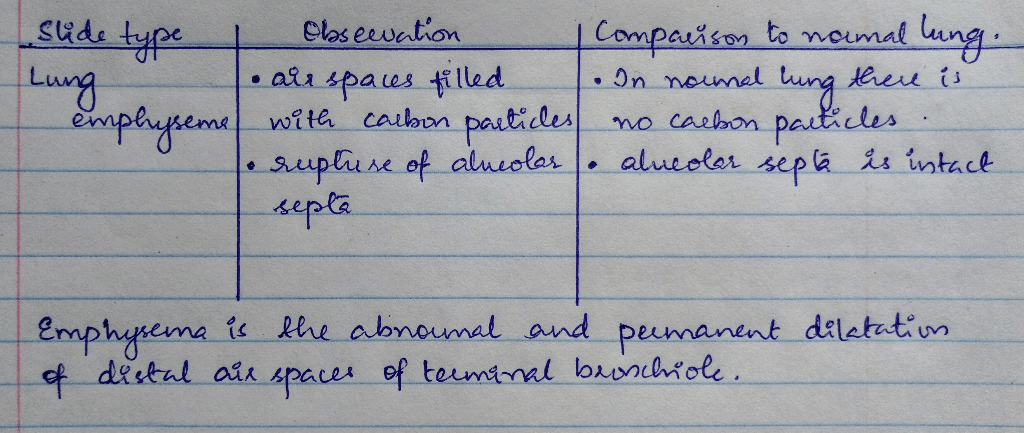
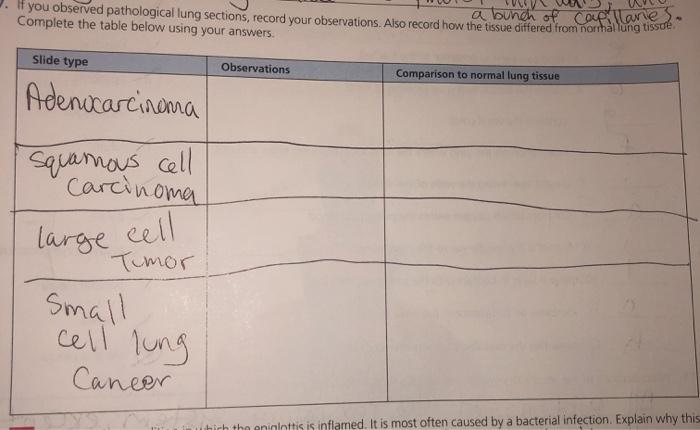
If you observed pathological lung sections – As we delve into the realm of pathological lung sections, we embark on a journey through the intricate world of histopathology, unlocking the secrets hidden within these microscopic landscapes. This guide will illuminate the significance of histopathological examination, guiding you through the techniques, findings, and applications that empower us to unravel the mysteries of lung disease.
Through the lens of microscopy, we will explore the spectrum of pathological changes that characterize various lung ailments, unraveling the complex interplay between structure and function. From the intricacies of tissue sampling and preparation to the power of immunohistochemistry and molecular analysis, we will delve into the cutting-edge tools that empower us to diagnose and understand lung diseases with unparalleled precision.
Histopathological Examination: If You Observed Pathological Lung Sections
Histopathological examination plays a crucial role in analyzing pathological lung sections, providing insights into the underlying cellular and tissue changes associated with lung diseases. It involves the microscopic examination of tissue samples to identify and characterize pathological changes.
Specific histopathological techniques used for lung tissue analysis include:
- Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining: Provides general visualization of tissue morphology and cellular components.
- Immunohistochemistry: Detects the presence and localization of specific proteins or markers in tissue sections.
- Special stains: Highlight specific tissue components, such as elastic fibers, collagen, or microorganisms.
Microscopy is essential in histopathological examination, allowing pathologists to visualize and interpret the morphological alterations in lung tissue. It enables the identification of abnormal cell growth patterns, inflammation, fibrosis, and other pathological changes.
Tissue Sampling and Preparation
Obtaining lung tissue samples for pathological examination can be done through various methods, including:
- Biopsy: Removal of a small tissue sample using a needle or surgical procedure.
- Resection: Surgical removal of a portion of lung tissue.
- Autopsy: Examination of lung tissue after death.
Proper tissue fixation and processing techniques are crucial to preserve the tissue’s morphology and prevent degradation. Fixation involves immersing the tissue sample in a chemical solution, such as formalin, to stabilize the proteins and prevent autolysis.
Staining methods enhance the visualization of pathological features by selectively coloring specific tissue components. H&E staining, for instance, stains nuclei blue and cytoplasm pink, allowing for easy identification of cellular structures.
Pathological Findings in Lung Diseases
Histopathological examination of lung tissue can reveal a wide range of pathological findings associated with various lung diseases. Common findings include:
- Inflammation: Infiltration of immune cells, such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, and macrophages.
- Fibrosis: Excessive deposition of collagen fibers, leading to scarring and loss of lung function.
- Emphysema: Destruction of lung tissue, resulting in enlarged air spaces and reduced gas exchange.
- Neoplasia: Abnormal cell growth, including both benign and malignant tumors.
Specific lung diseases exhibit characteristic histopathological features. For instance, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by emphysema and airway inflammation, while lung cancer may present as a mass or infiltrating neoplastic cells.
Differential diagnosis involves comparing the histopathological findings with known patterns of lung diseases to distinguish between different entities based on their characteristic features.
Immunohistochemistry and Molecular Analysis
Immunohistochemistry is a powerful tool in lung pathology, enabling the identification and localization of specific proteins or markers in tissue sections. It involves the use of antibodies that bind to target proteins, which are then visualized using a chromogenic or fluorescent substrate.
Molecular analysis techniques, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or sequencing, are used to detect and characterize genetic alterations associated with lung diseases. These techniques can identify mutations, deletions, or amplifications in genes, providing insights into the molecular pathogenesis of lung diseases.
Immunohistochemistry and molecular analysis aid in the diagnosis and characterization of lung diseases, providing additional information beyond routine histopathological examination.
Reporting and Interpretation of Results, If you observed pathological lung sections
Pathology reports for lung tissue examination typically include:
- Gross description: Macroscopic appearance of the tissue sample.
- Microscopic description: Histopathological findings, including cellular changes, inflammation, and other abnormalities.
- Diagnosis: Pathologist’s interpretation of the findings, based on established criteria.
Interpretation of pathological findings involves correlating the observed changes with known disease patterns and considering the clinical context. Communication between pathologists and clinicians is essential to ensure accurate interpretation and appropriate patient management.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of histopathological examination in lung pathology?
Histopathological examination allows for the microscopic evaluation of lung tissue, providing crucial insights into the cellular and structural changes associated with lung diseases. It enables the identification of specific pathological patterns, differentiation between various lung conditions, and assessment of disease severity and progression.
How are lung tissue samples obtained for pathological examination?
Lung tissue samples can be obtained through various methods, including biopsy, bronchoscopy, and surgical resection. The choice of technique depends on the specific clinical context and the location and accessibility of the lesion.
What is the role of immunohistochemistry in lung pathology?
Immunohistochemistry utilizes antibodies to detect specific proteins or markers within lung tissue sections. This technique allows for the identification and localization of specific cell types, proteins, and molecular markers, aiding in the diagnosis and characterization of lung diseases.