Locating an earthquake lab answer key – Locating an earthquake’s epicenter is a critical task in seismology, providing valuable information for understanding earthquake processes and assessing seismic hazards. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for locating an earthquake’s epicenter, covering the methods, equipment, and factors affecting accuracy.
By exploring the principles of seismic wave analysis and real-time monitoring, readers will gain a thorough understanding of the techniques used to determine an earthquake’s location.
Locating an Earthquake’s Epicenter: Locating An Earthquake Lab Answer Key
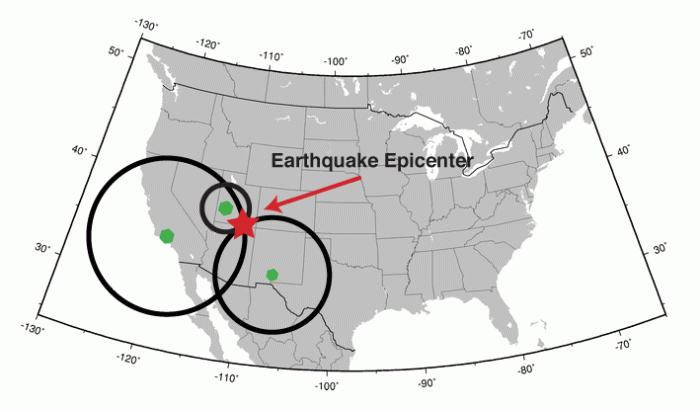
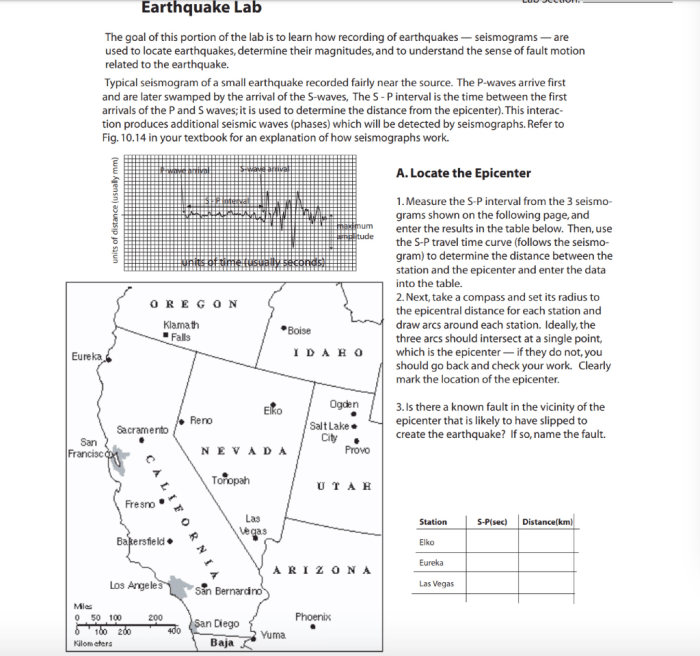
An earthquake’s epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter, where the earthquake originates. It is a crucial parameter for understanding the earthquake’s location, magnitude, and potential impact.
Locating an earthquake’s epicenter involves determining its latitude, longitude, and depth. This is achieved through various methods, including:
Seismic Wave Analysis
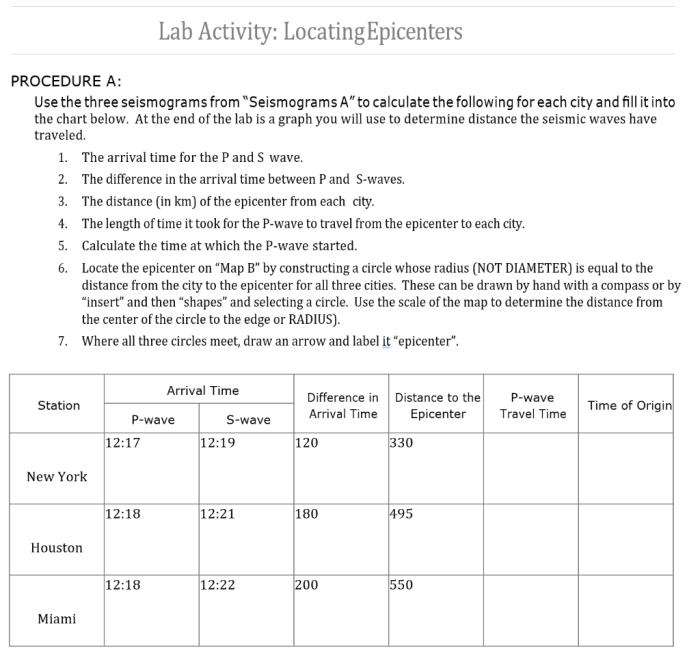
Seismic waves are generated by earthquakes and travel through the Earth’s interior and along its surface. By analyzing the arrival times and amplitudes of these waves at multiple seismic stations, scientists can triangulate the earthquake’s epicenter.
Triangulation
Triangulation is a technique used to determine the location of an object by measuring the angles between it and two or more known points. In the case of earthquakes, the known points are seismic stations, and the angles are determined from the arrival times of seismic waves.
Time-Distance Relationships, Locating an earthquake lab answer key
The time it takes for seismic waves to travel from the earthquake’s source to a seismic station depends on the distance between them and the velocity of the waves in the Earth’s interior. By measuring the time difference between the arrival of different seismic waves, scientists can estimate the distance to the earthquake’s epicenter.
Factors Affecting Epicenter Accuracy
The accuracy of epicenter location depends on several factors, including:
- Distance from seismic stations: The farther the earthquake is from seismic stations, the less accurate the epicenter location.
- Number of seismic stations: The more seismic stations that record the earthquake, the more accurate the epicenter location.
- Quality of seismic data: The quality of the seismic data, such as signal-to-noise ratio and data completeness, affects the accuracy of the epicenter location.
Essential FAQs
What is an earthquake’s epicenter?
An earthquake’s epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter, the location where the earthquake rupture initiates.
How are earthquakes located?
Earthquakes are located using seismic waves recorded by seismograph stations. The arrival times and amplitudes of these waves are analyzed to determine the earthquake’s epicenter and magnitude.
What factors affect the accuracy of earthquake location?
The accuracy of earthquake location depends on factors such as the distance and number of seismic stations, the quality of seismic data, and the complexity of the Earth’s structure.
What is the importance of real-time earthquake monitoring?
Real-time earthquake monitoring is crucial for early warning systems and rapid response to earthquakes, providing valuable time for evacuation and mitigation measures.
How is historical earthquake data used in earthquake studies?
Historical earthquake data provides insights into earthquake patterns, recurrence rates, and seismic hazards, aiding in long-term planning and risk assessment.