Ipm for the urban professional – Integrated Pest Management (IPM) for urban professionals is a crucial approach to maintaining a healthy and pest-free urban ecosystem. This guide will explore the benefits, techniques, challenges, and future trends of IPM in urban environments.
IPM for urban professionals encompasses a range of strategies to control pests while minimizing environmental impact. By understanding the principles and practices of IPM, urban professionals can create and maintain thriving urban spaces.
Definition of IPM for Urban Professionals
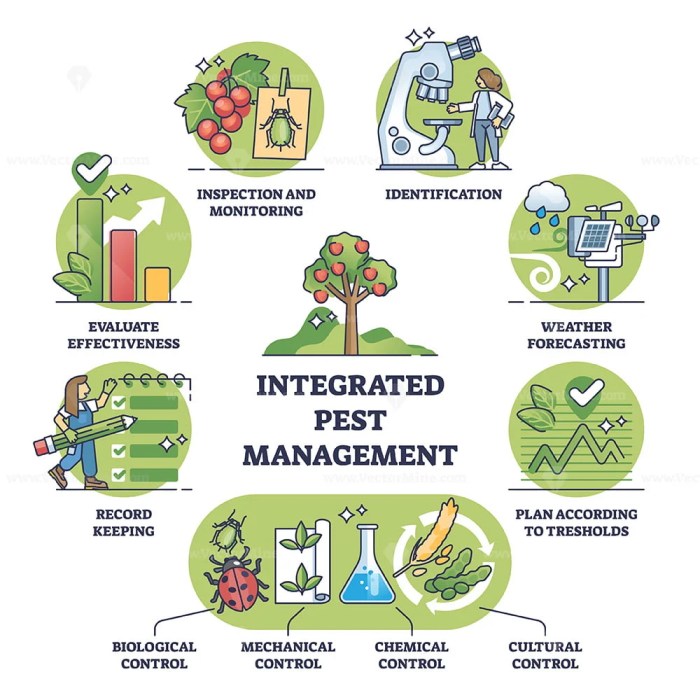
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach to pest control that focuses on preventing pests from becoming a problem in the first place, rather than relying solely on chemical pesticides. IPM for urban professionals involves using a variety of methods to manage pests, including:
- Inspection and monitoring to identify pests and their sources.
- Exclusion to prevent pests from entering buildings or other structures.
- Sanitation to remove food and water sources that attract pests.
- Biological control to use natural enemies to control pests.
- Chemical control to use pesticides only when necessary.
IPM is an important part of maintaining a healthy and pest-free urban ecosystem. By using a variety of methods to manage pests, IPM can help to reduce the use of pesticides, which can have harmful effects on human health and the environment.
Importance of IPM for Urban Professionals
IPM is important for urban professionals because it provides a comprehensive and effective approach to pest management. By using a variety of methods to manage pests, IPM can help to reduce the use of pesticides, which can have harmful effects on human health and the environment.
IPM can also help to prevent pests from becoming a problem in the first place, which can save time and money in the long run.
Benefits of IPM for Urban Professionals

IPM offers a plethora of advantages for urban professionals, particularly those working in property management, hospitality, and healthcare. Its focus on prevention, monitoring, and targeted treatment ensures effective pest control while minimizing environmental impact and safeguarding human health.
Numerous studies have substantiated the benefits of IPM in urban areas. For instance, a study conducted by the University of California, Davis, demonstrated that IPM reduced pesticide use by 50% in urban parks, significantly lowering the risk of pesticide exposure for park visitors and employees.
Case Studies, Ipm for the urban professional
Success stories further underscore the effectiveness of IPM in urban settings. The city of Portland, Oregon, implemented an IPM program in 2002, resulting in a 70% reduction in pesticide use within five years. This not only improved public health but also saved the city an estimated $2 million annually.
In the healthcare sector, IPM has proven invaluable in controlling pests that can transmit diseases. A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that IPM reduced the prevalence of cockroaches in hospitals by 80%, significantly decreasing the risk of hospital-acquired infections.
The daily routines of urban professionals require efficient time management and organization. One crucial aspect of urban living is staying informed about local safety concerns. The cda police daily activity log provides up-to-date information on police activities in the area, ensuring urban professionals can stay aware of any potential threats or incidents that may impact their daily commutes and activities.
IPM Techniques for Urban Professionals: Ipm For The Urban Professional
IPM for urban professionals involves a holistic approach to pest management that emphasizes prevention, monitoring, and targeted control measures. By implementing IPM techniques, urban professionals can effectively manage pests while minimizing the use of pesticides and their potential risks.
IPM principles include:
- Monitoring to detect and identify pest problems early on.
- Identification of pests and their biology to understand their behavior and vulnerabilities.
- Targeted pest control methods that focus on specific pests and minimize harm to non-target organisms.
Exclusion
Exclusion techniques aim to prevent pests from entering or establishing themselves in urban environments. Common methods include:
- Sealing cracks and holes in buildings and structures.
- Installing screens on windows and doors.
- Trimming vegetation away from buildings to reduce hiding places for pests.
Sanitation
Sanitation practices reduce food and water sources for pests, making urban environments less attractive to them. These practices include:
- Properly storing food and waste.
- Regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces.
- Eliminating standing water sources, such as clogged gutters or leaky pipes.
Biological Control
Biological control involves the use of natural enemies, such as predators or parasites, to suppress pest populations. Common methods include:
- Introducing ladybugs to control aphids.
- Using parasitic wasps to control caterpillars.
- Releasing predatory mites to control spider mites.
Challenges and Considerations in Urban IPM

Implementing IPM in densely populated urban areas presents unique challenges and considerations. Urban environments are characterized by a high concentration of buildings, infrastructure, and human activity, which can impact the implementation and effectiveness of IPM strategies.
Urban planning and regulations play a crucial role in supporting IPM programs. Zoning ordinances, building codes, and landscape design guidelines can be used to promote the use of IPM-compatible practices, such as the incorporation of green spaces, the selection of pest-resistant plants, and the minimization of pesticide use.
Community Engagement
Community engagement is essential for the success of IPM programs in urban areas. Residents, businesses, and other stakeholders must be informed about the benefits of IPM and actively involved in its implementation. Education campaigns, outreach programs, and community-based monitoring can help raise awareness and foster support for IPM.
Future Trends and Innovations in Urban IPM

The future of urban IPM holds exciting prospects, with emerging technologies and advancements promising to revolutionize pest management practices. Smart pest management systems, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) are poised to transform the way we monitor, prevent, and control pests in urban environments.
Smart Pest Management Systems
Smart pest management systems leverage IoT (Internet of Things) devices, sensors, and real-time data to enhance pest monitoring and control. These systems can:
- Detect pest presence and activity in real-time.
- Identify pest species and monitor population dynamics.
- Provide early warnings of potential infestations.
- Automate pest control measures, such as traps and repellents.
Data Analytics
Data analytics plays a crucial role in urban IPM by providing insights into pest behavior, environmental factors, and control effectiveness. By analyzing data collected from smart pest management systems, researchers and pest managers can:
- Identify patterns and trends in pest populations.
- Develop predictive models to forecast pest outbreaks.
- Optimize pest control strategies based on data-driven insights.
- Evaluate the efficacy of different IPM techniques.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is revolutionizing urban IPM by enabling the development of intelligent pest management solutions. AI-powered systems can:
- Automate pest identification and classification.
- Predict pest behavior and movement patterns.
- Recommend customized pest control strategies based on real-time data.
- Integrate with smart pest management systems for enhanced efficiency.
FAQ Compilation
What are the benefits of IPM for urban professionals?
IPM reduces the use of pesticides, protects human health and the environment, and promotes sustainable pest management practices.
What are some common IPM techniques for urban professionals?
IPM techniques include exclusion, sanitation, biological control, and targeted pest control methods.
What are the challenges of implementing IPM in urban areas?
Challenges include dense populations, limited resources, and the need for community engagement.